FloatingIP
1. Introduction
A FloatingIP, also known as "VIP (Virtual IP)," is a static public address that allows exposing services such as hosts, LoadBalancers, etc., under the same IP. A FloatingIP is primarily assigned to a machine (MASTER) as long as it is operational and switches to another machine (BACKUP) in case the MASTER fails.
2. KeepAlived
KeepAlived is a routing software that enables simple and robust setups for load balancing, relying on the Linux kernel module IPVS and the protocol VRRP.
2.1. Internet Protocol Virtual Server (IPVS)
IPVS is a Linux kernel module used for low-level network operations. This module is widely used but not well-known; iptables interface with it to manage firewalls. In the context of high availability, this module enables load balancing in the Linux kernel by operating on layer 4 of the OSI model.
2.2. Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
VRRP is a standard protocol designed to increase the availability of the default gateway for hosts on the same network. The principle is to define the default gateway for network hosts as a virtual IP address referencing a group of routers.
2.3. Operation
During configuration, two parameters are required for each server:
- The State, which specifies the type, i.e., MASTER or BACKUP.
- The Priority, which determines the BACKUP that will take over in case the MASTER fails.
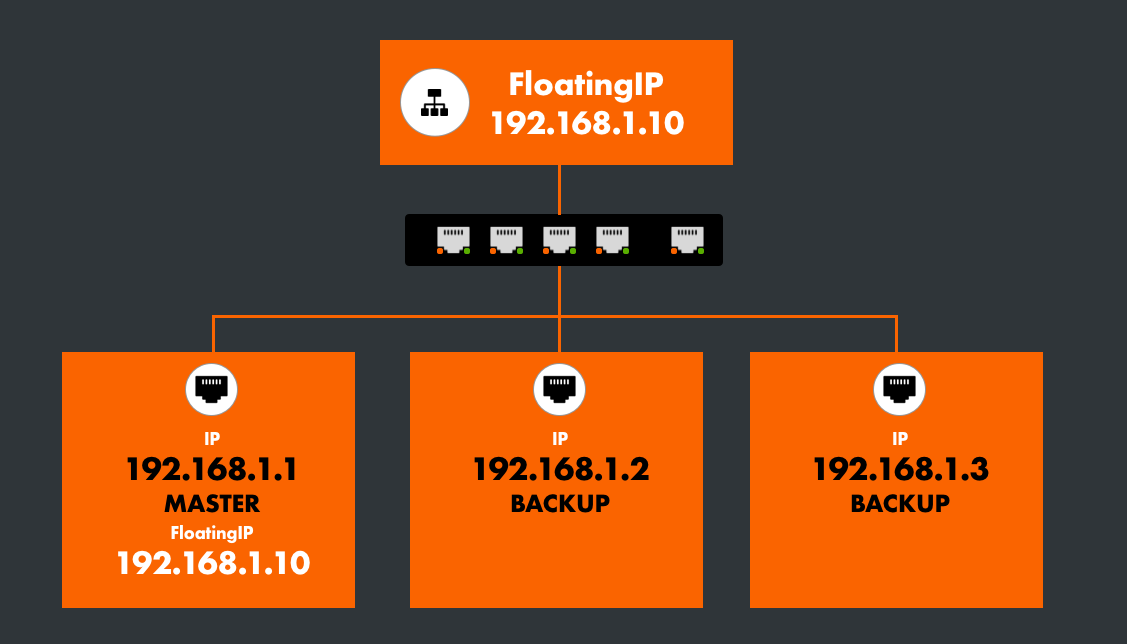
All Instances in Service
When all instances are operational, the default MASTER holds the FloatingIP.
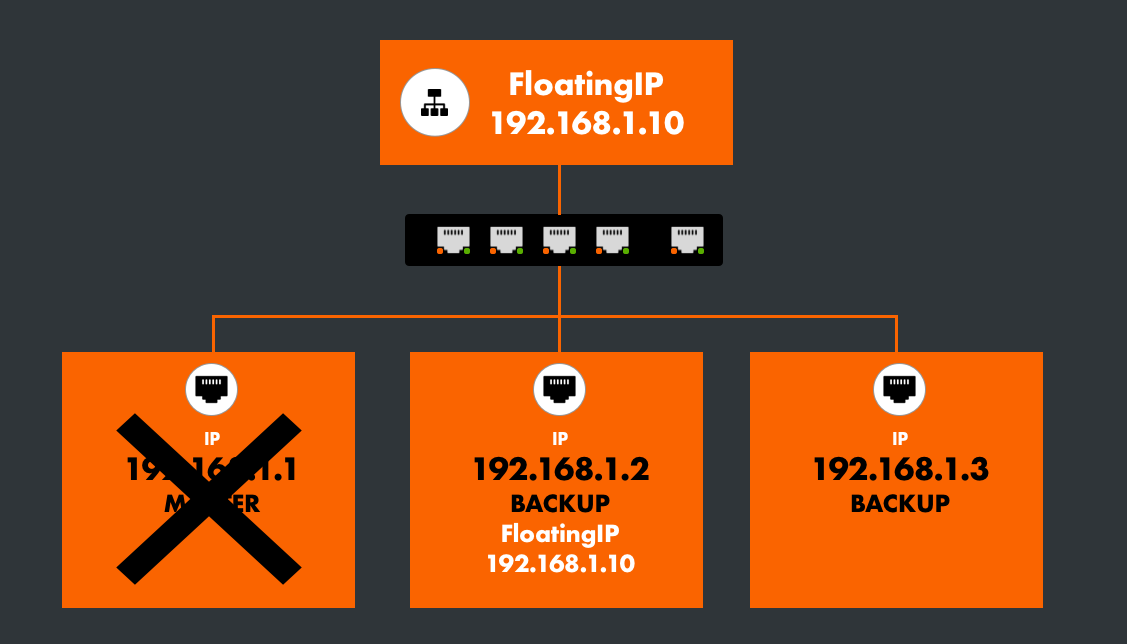
MASTER Out of Service
In case the MASTER fails, the FloatingIP switches to the BACKUP with the highest priority.
3. Installation
With the Protobox framework, the FloatingIP pool is configured by declaring the group in the main inventory.
----------------------------------------
| path: inventories/group_vars/vip.yml |
----------------------------------------
vips:
network-1:
ip: 192.168.x.x
subnet_mask: /24
virtual_router_id: 1
members:
host-1:
state: MASTER
priority: 200
host-2:
state: BACKUP
priority: 100
network-2:
ip: 192.168.x.x
subnet_mask: /24
virtual_router_id: 2
members:
host-1:
state: BACKUP
priority: 100
host-2:
state: MASTER
priority: 200
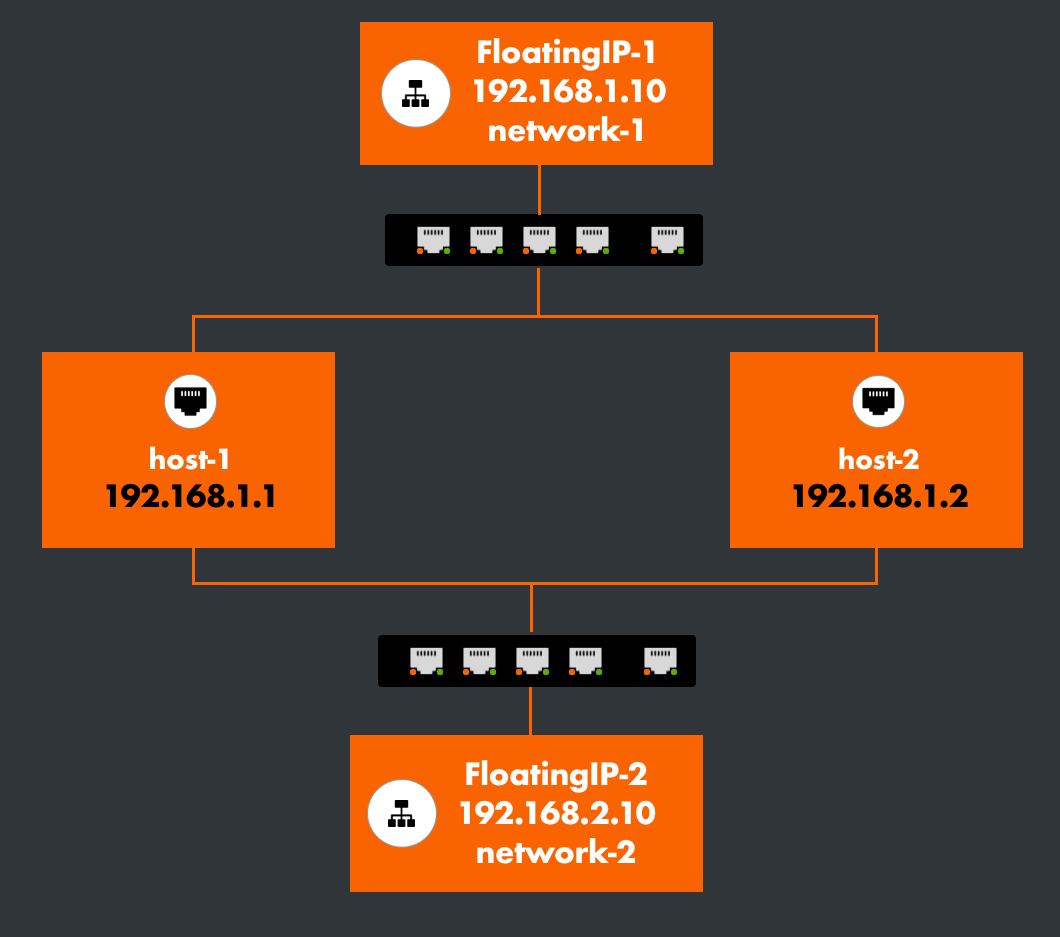
Result
The above declaration creates two FloatingIPs on two different networks.
- host-1 is the MASTER on the network network-1 and the BACKUP on network-2.
- host-2 is the MASTER on the network network-2 and the BACKUP on network-1.
- Configuration generated on host-1
-----------------------------------------
| path: /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf |
| host: host-1 |
-----------------------------------------
vrrp_script chk_haproxy {
script "killall -0 haproxy"
interval 2
weight 2
}
vrrp_instance network-1-host-1 {
state MASTER
interface public
virtual_router_id 1
priority 200
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type SUPERVISOR
auth_pass 4000
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.x.x/24
}
}
vrrp_instance network-2-host-1 {
state MASTER
interface box
virtual_router_id 2
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type SUPERVISOR
auth_pass 4000
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.x.x/24
}
}
- Configuration generated on host-2
-----------------------------------------
| path: /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf |
| host: host-2 |
-----------------------------------------
vrrp_instance network-1-host-2 {
state BACKUP
interface network-1
virtual_router_id 1
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 4000
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.x.x/24
}
}
vrrp_instance network-2-host-2 {
state MASTER
interface network-2
virtual_router_id 2
priority 200
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 4000
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.x.x/24
}
}