CI (Gitlab CI)
1. Introduction
CI is one of the pillars of the software factory. It is the phase that, in most cases, builds the package of an application. Modern applications are often deployed as containers. Therefore, the construction and storage of their images are carried out during the CI stages. To build containerized images, it is essential to have a Git repository and a container registry. In this project, these two elements are local; the infrastructure includes a server for both functionalities. Our choice is Gitlab Server, which integrates both.
2. Gitlab Server
2.1. Installation
The installation is done using the factory/gitlab role, which, depending on the specified runtime, launches Gitlab in container or systemd mode.
-------------------------------------------------------------
| path: playbooks-supervisor-pool/install.yml |
-------------------------------------------------------------
- name: Setup supervisor host
hosts: supervisor-1
become: true
user: supervisor
gather_facts: false
roles:
...
- {role: factory/gitlab, runtime: "systemd", install: true}
...
2.2. Configuration
-------------------------------------------------------------
| path: roles/factory/gitlab/templates/systemd/gitlab.rb.j2 |
-------------------------------------------------------------
external_url 'http://git.protobox/gitlab'
pages_external_url 'http://pages.protobox'
gitlab_rails['initial_root_password'] = 'XXXXXXX'
git_data_dirs({
"default" => {
"path" => "/storage/shared/gitlab/data"
}
})
letsencrypt['enable'] = false
nginx['listen_port'] = 80
3. Container Registry
The container registry used in this project is the one embedded in Gitlab Server (disabled by default). Activation is done within the configuration file.
-------------------------------------------------------------
| path: roles/factory/gitlab/templates/systemd/gitlab.rb.j2 |
-------------------------------------------------------------
registry_external_url 'https://registry.protobox'
registry_nginx['listen_port'] = 443
registry_nginx['redirect_http_to_https'] = true
registry_nginx['ssl_certificate'] = "{{ tls['registry']['crt'] }}"
registry_nginx['ssl_certificate_key'] = "{{ tls['registry']['key'] }}"
4. Runners
Runners are agents that run on various machines to execute operations remotely controlled by Gitlab Server.
To install it on a server, Protobox uses the factory/gitlab-runners role.
Declaration (Example)
----------------------------------------------------
| path: playbooks-proxiserver-pool/nat-install.yml |
----------------------------------------------------
- name: Install nat-gateway-pool
hosts: nat_gateway_pool
become: true
user: supervisor
gather_facts: false
roles:
...
- {role: factory/gitlab-runners, runtime: "systemd"}
...
Generated Configuration (Example)
----------------------------------------
| path: /etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml |
----------------------------------------
concurrent = 1
check_interval = 0
shutdown_timeout = 0
[session_server]
session_timeout = 1800
[[runners]]
name = "gateway-3"
url = "http://git.protobox/gitlab/"
id = 6
token = "XXXXXXXXXXXXXX"
token_obtained_at = 2023-02-20T21:22:03Z
token_expires_at = 0001-01-01T00:00:00Z
executor = "docker"
[runners.docker]
tls_verify = false
image = "alpine"
privileged = true
disable_entrypoint_overwrite = false
oom_kill_disable = false
disable_cache = false
volumes = ["/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock", "/cache"]
shm_size = 0
network_mode = "host"
5. Kustomize
In our applications, Kustomize is used to update the versions of the images used by Kubernetes. This tool also allows us to customize our Kubernetes objects based on the type of environment (dev, test, staging, production, etc.).
6. Pipelines
6.1. Configuration
For each application, the following directory must be created, containing the .gitlab-ci.yml file to define the pipeline. This is a convention set for all our applications.
factory/CD/.gitlab-ci.yml
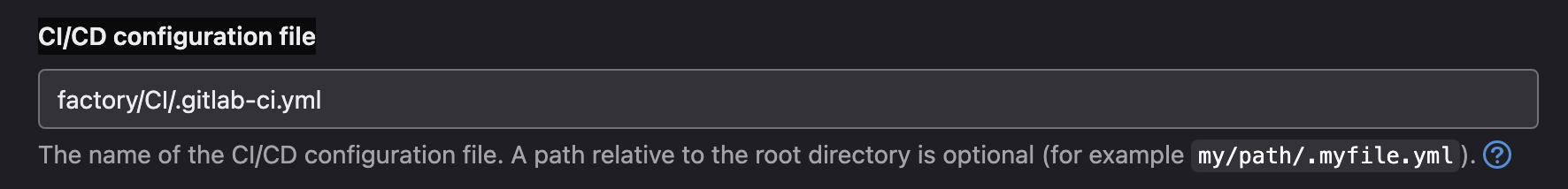
On Gitlab Server, this path must also be declared.
project_name > Settings > CI/CD > CI/CD configuration file
6.2. Process
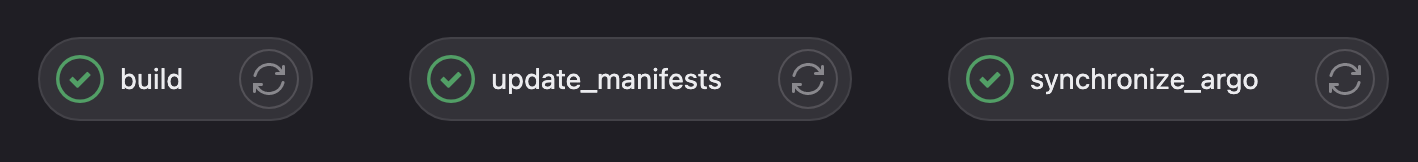
The processes vary and may be specific to each project. However, most applications follow these three phases.
6.2.1. Build
The build phase consists of several steps. It is primarily used to build the container image in question. During this phase, the image is also pushed to the registry.
build:
image: docker:stable
stage: build
services:
- docker:dind
before_script:
- docker info
- docker login -u $REGISTRY_USERNAME -p $REGISTRY_PASSWORD $REGISTRY_URL
script:
- docker build -t $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE/$CI_PROJECT_NAME:$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME .
- docker build -t $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE/$CI_PROJECT_NAME:latest .
- docker push $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE/$CI_PROJECT_NAME:$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME
- docker push $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE/$CI_PROJECT_NAME:latest
6.2.2. Update Manifests
This step updates the version of the image used by Kubernetes. During this phase, the manifests used are updated so they can be deployed in the cluster. To achieve this, the pipeline uses Kustomize.
update_manifests:
image: alpine:latest
stage: update_manifests
variables:
GIT_STRATEGY: none
retry: 2
before_script:
- apk add --no-cache git curl bash openssh
- curl -s "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/master/hack/install_kustomize.sh" | bash
- mv kustomize /usr/local/bin/
- cd
- git clone --single-branch --branch $CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME http://supervisor:$SUPERVISOR_ACCESS_TOKEN@git.protobox/gitlab/protobox1/docserver.git
- git config --global user.name $REGISTRY_USERNAME
- git config --global user.email $CI_USER_EMAIL
script:
- echo $CI_PROJECT_NAME
- cd $CI_PROJECT_NAME
- git fetch --prune
- git checkout ${ARGO_TARGET_REVISION}
- cd factory/CD/base
- kustomize edit set image $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE/$CI_PROJECT_NAME:$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME
- cat kustomization.yaml
- cat deployment.yml
- git add .
- git commit -m '[skip ci] [ARGOCD] ${CI_COMMIT_MESSAGE}'
- git push origin $ARGO_TARGET_REVISION
6.2.3. Synchronize ArgoCD
Synchronization involves indirectly triggering deployment by delegating it to ArgoCD. In our applications, ArgoCD is set to manual synchronization (auto mode disabled). Therefore, after each manifest update, the pipeline must notify ArgoCD to retrieve them.
synchronize_argo:
image: alpine:latest
stage: synchronize_argo
variables:
GIT_STRATEGY: none
retry: 2
before_script:
- apk add jq curl git delta
- curl -sSf -L -o /usr/local/bin/argocd "https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/download/v${ARGOCD_VERSION}/argocd-linux-amd64"
- chmod +x /usr/local/bin/argocd
- argocd login "${ARGO_SERVER_URL}" --insecure --username "${ARGO_USER_ID}" --password "${ARGO_USER_PASSWORD}" --plaintext
script:
- argocd app get argo-${CI_PROJECT_NAME} --refresh > /dev/null 2>&1
- argocd app sync argo-${CI_PROJECT_NAME} --assumeYes
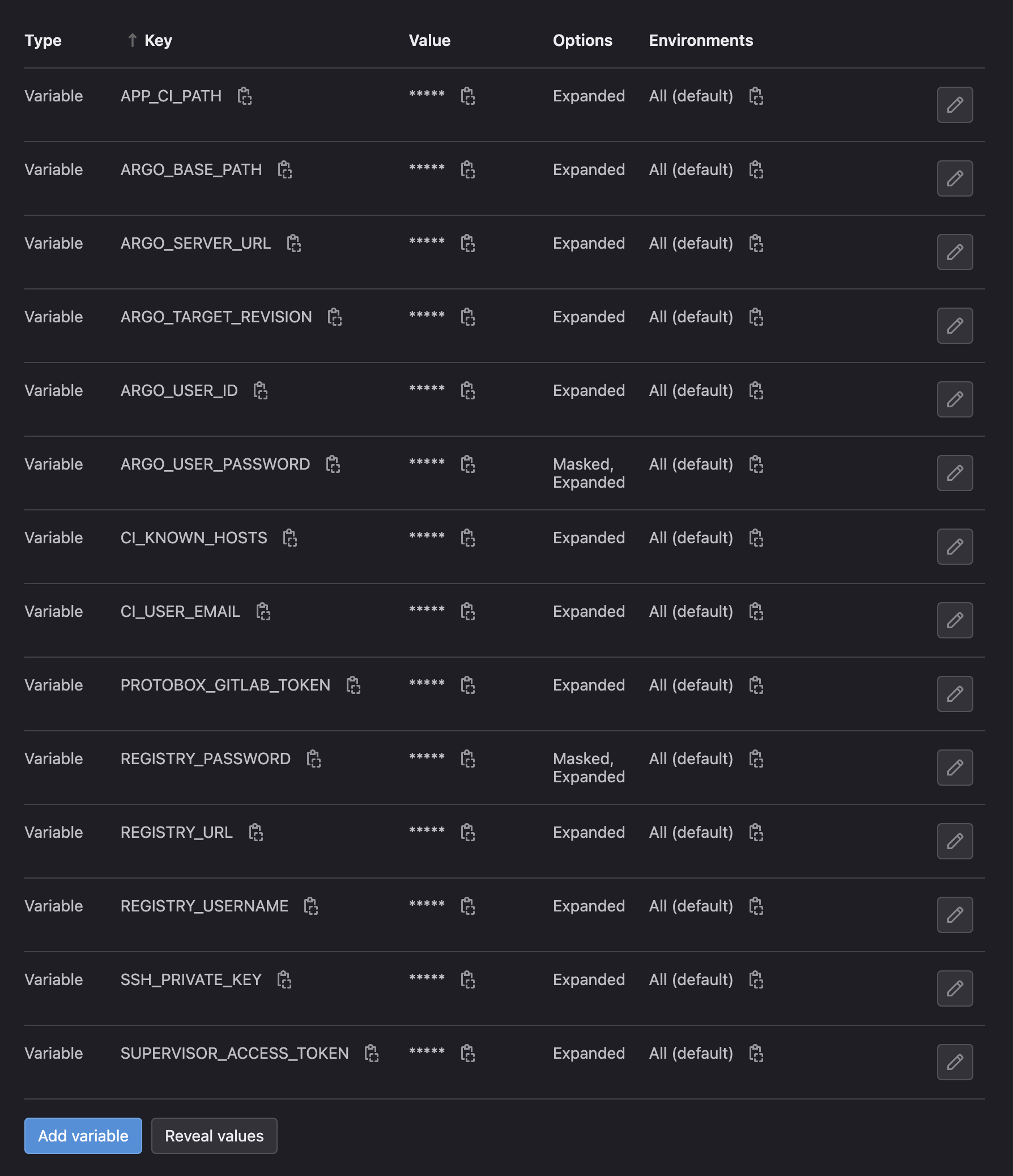
Variables